The fundamental elements of electricity are quite straightforward and logical to comprehend. electrical terms relate and get along with each other like a harmonious family. Before you tackle any electrical or home wiring Project, get acquainted with these terms so you can approach them more intelligently, safely, and without hesitation.
What Is a Watt?
Watts measure electrical power. Consider watts as the force behind electricity when used for heating or lighting rooms in your house. For instance, take a portable electric space heater Rated at 500 watts, this space heater uses 500 watts of electricity whenever it is activated.
You'll also come across wattage when choosing. light bulbs To locate an incandescent bulb that provides similar illumination to the one that has burnt out, you should look at the wattage. Additionally, the wattage rating of an appliance is typically indicated on its nameplate.
What Is a Volt?
voltage acts as the force that drives electrical current through a conductor.
In North America, utility systems generally provide electricity to your home’s service panel at voltages of 240 and 120. Large electric devices such as ranges , clothes dryers, water heaters , air conditioning and space heating systems Typically, they function at 240 volts. All other devices run on 120 volts.
What Is an Amp?
Amperage indicates how quickly electricity moves through an electrical circuit. To liken it to plumbing terms, voltage acts as water pressure, whereas amperage represents the speed at which the water travels. People often abbreviate "amperage" as "amps."
During installation, modification, or replacement of branch circuits in your house, within your electrical panel, you'll encounter either fuses or circuit breakers Of varying dimensions. Standard general-purpose lighting and electrical outlet circuits have a rating of 15 amps. In more recent building practices, you will additionally encounter specialized 20-amp circuits designed specifically for areas like kitchens, bathrooms, and laundry rooms. garage receptacle outlets along with appliances such as a dishwasher or refrigerator.
Electric clothes dryers and electric water heaters usually have a rating of 30 amps. Air-conditioning units Electric ranges and electric countertops or wall-mounted ovens can have ratings of 30, 40, or 50 amps.
Every electrical component in your house should be synchronized to ensure safe operation. The amperage rating of the fuse or circuit breaker determines the wire gauge and limits the circuit’s capabilities. Should you require additional amps, larger wires will be necessary.
What Is an Ohm?
An ohm (denoted by the Greek symbol Omega, or Ω) gauges the intrinsic resistance present in any material. electrical wire Copper wiring, which is a great conductor of electricity, is commonly seen in numerous households. On the other hand, aluminum wiring, also a proficient conductor, is utilized in various settings including commercial spaces, factories, and power utilities. Each type has natural opposition to electric current flow.
Different metal wires possess varying levels of electrical resistance, similar to how a miniature garden hose restricts water flow when contrasted with a substantial fire hose.
While troubleshooting electrical circuits, appliances, light switches, fuses, relays, and various other electrical parts using a multimeter, certain measurements and readouts may appear as ohms. If you test the integrity of a fresh fuse, the multimeter will read about zero Ohms of resistance. This indicates that the fuse has continuity and is in working condition.
On the contrary, when inspecting a potentially faulty fuse or malfunctioning light switch, you'll likely obtain an Ohm reading different from zero. This could signify a blown fuse or a defective light switch. Refer to the multimeter’s instruction manual for guidance on how to proceed. operate it safely and interpret the readings.
What Is the Relationship Between Watts, Volts, Amps, and Ohms?
Electrical mathematics is simple. Once you have information about two variables, you can determine the outcome. Knowing "x" and "y," allows you to calculate "z."
Numerous laws govern physics, science, and nature, with Ohm’s Law being crucial for grasping fundamental concepts of electricity. The Ohm’s Law Wheel simplifies this comprehension further.
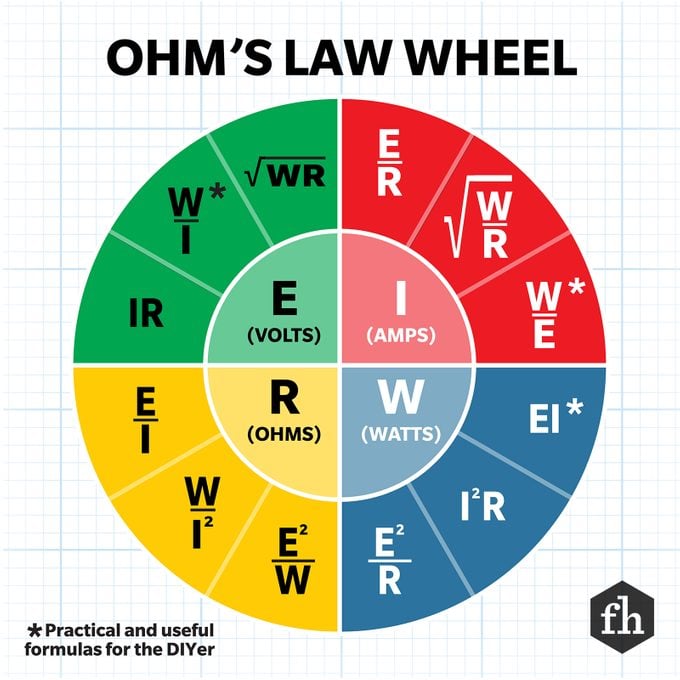
Sure, here’s how you can explain that scenario differently:
Imagine you're fitting an electric space heater in your garage. The local hardware shop has a 5,000-watt (or five kilowatts/5kW) model available which would be ideal for the area. Can you determine what size circuit this heater will require?
Based on the label, the space heater has a rating of 5kW and requires a voltage supply of 240 volts. You need to determine the amperage (denoted as 'I' for "current intensity"). Referring to the Ohm’s Law chart, use this equation:
I = W/V (amperes = watts divided by volts)
I = 5,000 watts ÷ 240 volts;
I = 20.8 amps;
Due to the possibility that the electric space heater might run continuously for at least three hours during chilly weather, a safety margin of 125% is used. Thus, 20.8 amps multiplied by 1.25 equals 26 amps.
Everything is completed! A typical 30-amp branch circuit will provide sufficient power to reliably and safely deliver continuous electrical supply to the space heater.
How to Operate Securely Within Your House's Electrical Network
- Electricity is an unseen force that we often overlook. Handling electricity doesn’t have to be risky or complicated provided you understand its workings, handle it cautiously, and follow simple safety measures. Discover how to do so effectively. safely use electrical tools and testers.
- Make sure your electrical tester or multimeter is working properly before turning off the power.
- Always disconnect power from circuits prior to working on them. Place a label, sign or circuit breaker lockout device At the electrical panel to prevent anyone from accidentally restoring the power. You can find various universal circuit breaker lockout devices at home improvement stores and online for under $10.
- Always use protective eyewear and nonconductive leather, rubber, latex, nitrile, or comparable dry gloves. Opt for garments made from natural fibers rather than synthetic ones.
- Wear appropriate heavy-duty shoes and avoid standing or kneeling on wet or moist surfaces while handling electricity. Utilize a dry, insulating wooden object instead. nonconductive mat, especially when working outdoors.
- Utilize tools featuring handles made of rubber or plastic. These nonconductive handle materials offer an additional layer of defense against electrical risks.


Post a Comment